Get a Free box of Gummies ($120 value) when you spend $200 or more. Now through Monday
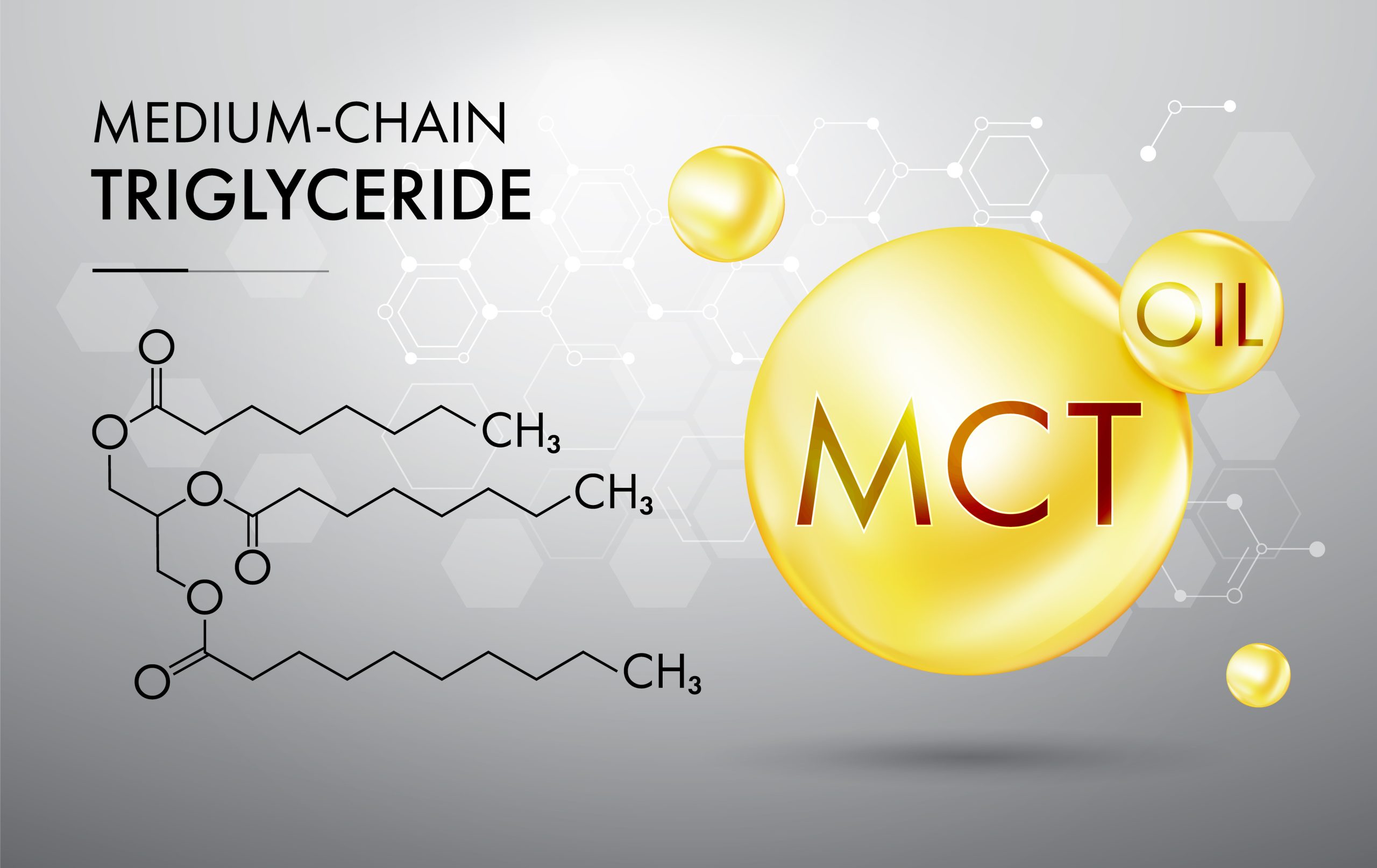
Alongside healthy oils, like avocado and extra virgin, medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil has risen to the top of the list of most popular dietary oils because it is quickly absorbed and metabolized by the body and provides an accessible energy source.
In this blog, we discuss the unique properties of MCT as well as potential health benefits that include but are not limited to, quick energy reserves and glucose regulation.
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are dietary fats that are found naturally in palm and coconut oil as well as dairy products. However, one of the richest sources of pure MCT oil is derived from coconut.
The medium-chain triglyceride oil processed from the coconut provides a concentrated source of medium-chain triglycerides (fats) which may provide some potential health benefits. MCT oil can be used as a quick and readily available fuel source for the body, it may also play a role in weight management and healthy glucose regulation.
A triglyceride is composed of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acids. There are three types of triglycerides: short-chain, medium-chain, and long-chain. The number of carbon atoms linked together in each of these fat structures determines digestion time. Long-chain triglycerides (LCTs) are made up of carbon chains ranging from 13 to 21 carbons, whereas medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are much shorter, consisting of only 6 to 12 carbon atoms.1,2 The body can use the MCTs immediately without having to break them down because of their shorter chains.
With the technical jargon out of the way, let’s explore some of the potential health benefits of MCT oil.
So how does the body use medium-chain triglycerides? Since MCTs are not digested in the stomach like long-chain triglycerides, they are known to be quick energy providers. They are transported to the liver where they are metabolized into available energy. When dietary fat is delivered to the liver, it is broken down and converted into chemicals known as ketones.3 These energy-efficient ketones become the energy-efficient workers, activating the switch that allows the body to use them as fuel first.4
The targeted population that has voiced an increased interest in the use of MCT oil are many health-conscious individuals and athletes. These individuals are looking to prevent the depletion of their glycogen stores and harvest an immediate energy source when needed to support endurance during exercise —and are looking for MCTs in this oil to do just that!
Some research has shown that the addition of MCT oil before eating may help promote the feeling of satiety or a sense of fullness.5,6 In one study, male participants who were diagnosed as overweight, were given MCT oil for breakfast and reported a greater sense of satiety than the other group who were those given LCT oil (corn oil). The participants who consumed the MCT oil had a lower caloric intake at lunch than those who were given LCTs.5
MCTs may influence the hunger and satiety hormones produced by our bodies; however, some studies suggest that MCT oil may support increased calorie or energy expenditure by increasing fat oxidation or turning up the heat to burn body fat rather than store it. Over time, this can reduce adipose or fat storage, and these pathways may be the mechanism driving lower caloric intake.5
The bottom line is that MCTs may have an acute impact on the decrease in food consumption, but additional research is required. Weight management is a process influenced by many factors outside of diet and consulting your healthcare provider is the first place to start.
Some studies suggest that MCT oil can be used to support normal glucose metabolism because it increases ketone body production and doesn’t rely on tapping into glycogen stores. MCTs may also help to increase caloric expenditure, which, when combined with a reduced dietary intake and exercise, may contribute to better glucose management. 7
Incorporating MCT oil into a diet for people looking to manage their blood glucose levels and improve insulin response may be beneficial, and though no direct link has been substantiated to support this, there is promise in the continued research.
Keep in mind the quality of the product you are looking to purchase should ideally be 100 % pure MCT oil from organic coconut.
Ensure that the product is third-party tested for quality and purity.
As with all dietary supplements, check with your healthcare provider (HCP) to see if you are a candidate for MCT oil. Also, it’s best to share with your healthcare provider the recommended serving directions written on the product label to see if they agree with this.
As always, remember to follow the medical plan that your healthcare provider has mapped out with you, and try your best to commit to positive lifestyle changes, to successfully address your health concerns.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, mitigate, or prevent any disease. Individual results may vary. The information provided in this blog is for educational and informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice.

Ken Swartz, MS is the co-founder, Chairman Emeritus, and former Chief Science Officer at C60 Power, a health and wellness company committed to delivering the highest quality Carbon 60 products available. Ken earned a Master of Science degree from the University of Colorado at Denver and a Bachelor of Science in Economics from Arizona State University.’
References